The Linux file system is a logical collection of files on a partition or disk. Every partition is a container for information and can span an entire hard drive if desired.
Linux file system is generally a built-in layer of a Linux operating system and Your hard drive has various partitions for storing operating information.
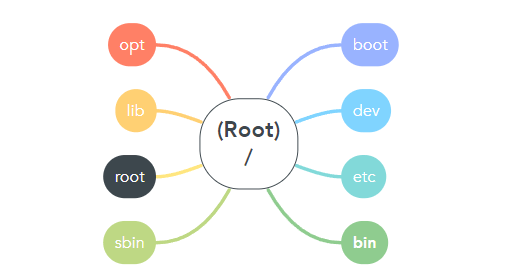
Linux file system

| Directory | Description |
| / | The root directory is the top-level directory in the FHS. All other directories are subdirectories of root, which is always mounted on some volume |
| /bin | Essential command-line utilities. Should not be mounted separately, otherwise, it could be difficult to get to these utilities when using a rescue disk. On RHEL 7, it is a symbolic link to /usr/bin. |
| /boot | Includes Linux startup files, including the Linux kernel. The default, 500MB, is usually sufficient for a typical modular kernel and additional kernels that you might install during the RHCE or RHCSA exam. |
| /dev | Hardware and software device drivers for everything from floppy drives to terminals. Do not mount this directory on a separate volume. |
| /etc | Most basic configuration files. Do not mount this directory on a separate volume. |
| /home | Home directories for almost every user. |
| /lib | Program libraries for the kernel and various command-line utilities. Do not mount this directory on a separate volume. On RHEL. 7, this is a symbolic link to /usr/lib. |
| /lib64 | Same as /lib, but includes 64-bit libraries. On RHEL 7, this is a symbolic link to/usr/lib64. |
| /media | The mount point for removable media, including DVDs and USB disk drives. |
| /misc | The standard mount point for local directories mounted via the automounter. |
| /mnt | A mount point for temporarily mounted filesystems. |
| /net | The standard mount point for network directories mounted via the automounter. |
| /opt | Common location for third-party application files. |
| /proc | A virtual filesystem listing information for currently running kernel-related processes, including device assignments such as IRQ ports, I/O addresses, and DMA channels, as well as kernel-configuration settings such as IP forwarding. As a virtual filesystem. Linux automatically configures it as a separate filesystem in RAM. |
| /root | The home directory of the root user. Do not mount this directory on a separate volume. |
| /run | A tmpfs filesystem for files that should not persist after a reboot. On RHEL 7, filesystem replaces /var/run, which is a symbolic link to /run. |
| /sbin | System administration commands. Don’t mount this directory separately. On RHEL 7. this is a symbolic link to /usr/bin. |
| /smb | The standard mount point for remote shared Microsoft network directories mounted via the automounter |
| /srv | Commonly used by various network servers on non-Red Hat distributions. |
| /sys | Similar to the /proc filesystem. Used to expose information about devices, drivers, and some kernel features. |
| /tmp | Temporary files. By default, Red Hat Enterprise Linux deletes all files in this directory periodically. |
| /usr | Programs and read-only data. Includes many system administration commands, utilities, and libraries. |
| /var | Variable data, including log files and printer spools. |