In this chapter, we’re going to dig into NAT Types, Network Address Translation ( NAT ), Dynamic NAT, and Port Address Translation (PAT), also known as NAT Overload. So be sure not to miss those!
NAT Types
- Static NAT (one-to-one)
- Dynamic NAT (many-to-many)
- Overloading (one-to-many)
When Do We Use NAT ?
- When you need to connect to the Internet and your hosts don’t have globally unique IP addresses
- When you’ve changed to a new ISP that requires you to renumber your network
- When you need to merge two intranets with duplicate addresses You typically use NAT on a border router. For example, NAT is used on the Corporate router connected to the Internet.
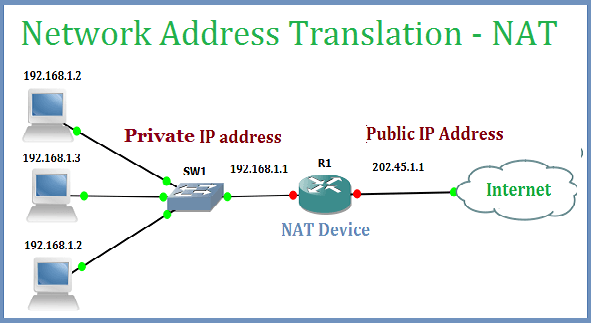
Types of Network Address Translation ( NAT Types )
Static NAT (one-to-one)
This NAT types is designed to allow one-to-one mapping between local and global addresses. Keep in mind that the static version requires you to have one real Internet IP address for every host on your network.
Dynamic NAT (many-to-many)
This version gives you the ability to map an unregistered IP address to a registered IP address from out of a pool of registered IP addresses. You don’t have to statically configure your router to map each inside address to an individual outside address as you would using static NAT, but you do have to have enough real, bona fide IP addresses for everyone who’s going to be sending packets to and receiving them from the Internet at the same time.
Overloading (one-to-many)
This is the most popular NAT types configuration. Understand that overloading really is a form of dynamic NAT that maps multiple unregistered IP addresses to a single registered IP address (many-to-one) by using different source ports. Now, why is this so special? Well, because it’s also known as Port Address Translation (PAT), which is also commonly referred to as NAT Overload. Using PAT allows you to permit thousands ofusers to connect to the Internet using only one real global IP address—pretty slick, right? Seriously, NAT Overload is the realreason we haven’t run out of valid IP addresses on the Internet.
How NAT Network Works
The names we have a tendency to use to explain the addresses used with NAT area unit fairly simple. Addresses used once NAT translations area unit referred to as world addresses. These area unit sometimes the general public addresses used on the net, that you don’t want if you aren’t occurring the net.
Local addresses area unit those we have a tendency to use before NAT translation. this implies that the within native address is truly the non-public address of the causing host that’s making an attempt to urge to the net. the skin native address would usually be the router interface connected to your ISP and is additionally sometimes a public address used because the packet begins its journey.. Click Here
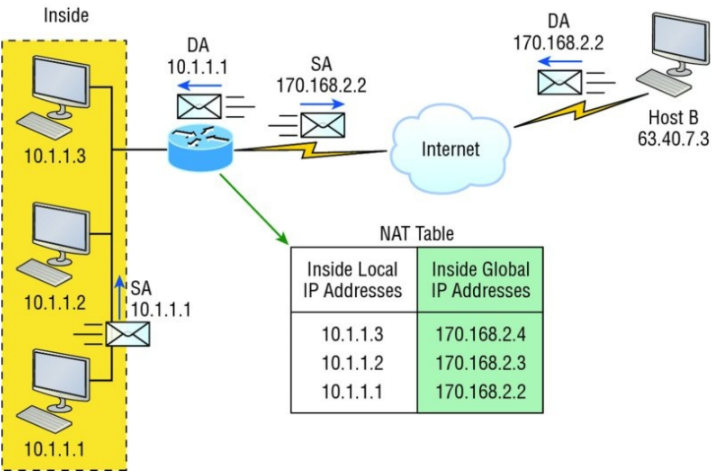
Basic NAT translation
In this figure, we can see host 10.1.1.1 sending an Internet-bound packet to the border router configured with NAT types . The router identifies the source IP address as an inside local IP address destined for an outside network, translates the source IP address in the packet, and documents the translation in the NAT table.
The packet is sent to the outside interface with the new translated source address. The external host returns the packet to the destination host and the NAT router translates the inside global IP address back to the inside local IP address using the NAT table. This is as simple as it gets!
NAT Overloading example (PAT)
This NAT Types, all within hosts get translated to at least one single scientific discipline address, therefore the term overloading. Again, the explanation we’ve simply run out of accessible world scientific discipline addresses on the net is owing to overloading (PAT).
Take a glance at the NAT varieties table inFigure higher than image. additionally to {the within|the within} native scientific discipline address and inside world scientific discipline address, we have a tendency to currently have port numbers. These port numbers facilitate the router establish that host ought to receive the come traffic. The router uses the supply port variety from every host to differentiate the traffic from every of them. perceive that the packet incorporates a destination port variety of eighty once it leaves the router, and therefore the communications protocol server sends back the information with a destination port variety of 1026, during this example. this enables the NAT translation router to differentiate between hosts within the NAT table so translate the destination scientific discipline address back to the within native address.
Port numbers area unit used at the Transport layer to spot the native host during this example. If we have a tendency to had to use real world scientific discipline addresses to spot the supply hosts, that’s referred to as static NAT and that we would run out of addresses. PAT permits North American nation to use the Transport layer to spot the hosts, that successively permits North American nation to on paper burn up to concerning sixty five,000 hosts with just one real scientific discipline address!
Thank you pertaining to spreading this kind of wonderful content on your website. I came across it on google. I may check to come back whenever you publish much more aricles.
Thank you so much for your support and like my content.