What’s SQL Server ?
SQL server a domain-specific Structured Query Language, it’s relational database management systems, it used in programming and designed for managing other operations, including optimizing and maintenance of databases.
What’s SQL server Database ?
Database is collection of information organized for easy access, management and maintenance.
Examples:
- Telephone directory
- Customer data
- Product inventory
- Visitors register
- Weather records

Types of SQL Server Data Models:
Record Based logical model
- Hierarchical data model
- Network data model
- Relational data model
Object based logical model
- Entity relationship model
SQL Constraints
| Constraint | Description |
| Not Null | Ensures that a colume does not have a NULL value |
| Default | Provides a default value for a column when none is specified. |
| Unique | Ensures that all the values in a column are different. |
| Primary | identifies each row / record in a database table uniquely. |
| Check | Ensures that all values in a colume satisfy certainconditions. |
| Index | Creates and retrieves data from the database very quickly. |
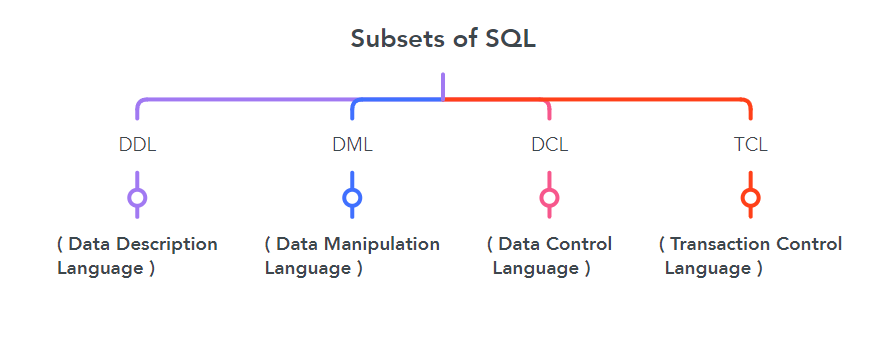
1. DDL – Data Definition Language
| Command | Discription |
| Create | Create objects in the database / database objects |
| Alter | Alters the structures of the database / database objects |
| Drop | Deletes objects from the database |
| Truncate | Remove all record from a table permanenly |
Login SQL server
[root@localhost conf.d]# mysql -u root -p
Enter password:
Create Database command
create database [databasename];

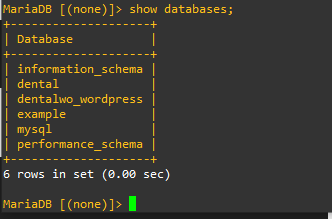
Show All Database
show databases;
show tables;
Select database
use example;
Create Table command
MariaDB [example]> create table employees(
emp_id int not null,
first_name varchar(20),
last_name varchar(20),
salary int,
primary key(emp_id)
);

Show Table recodes
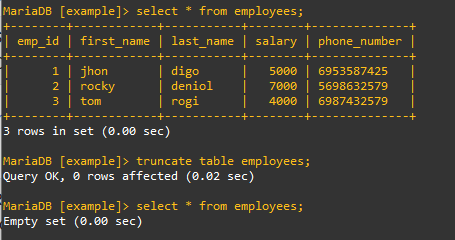
select * from employees;
describe employees;

Alter Command
alter table employees add column contact int;
describe employees;

alter table employees drop column contact;
alter table employees change contact phone_number int;
alter table employees add unique (phone_number);
alter table employees modify phone_number varchar(12);
alter table employees drop index phone_number;
Truncate Command
truncate table employees;
Deleted database command
drop table employees;
drop database example;
show databases;

Deleted User command
MariaDB [(none)]> drop user demo;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)
Show all user
MariaDB [(none)]> select user, host from mysql.user;
+———-+———————–+
| user | host |
+———-+———————–+
| julfikar | % |
| root | 127.0.0.1 |
| root | ::1 |
| root | localhost |
| root | localhost.localdomain |
+———-+———————–+
5 rows in set (0.00 sec)
2. DML – Date Manipulation Language
| Command | Description |
| Insert | Insert data into a table |
| Update | Updates existing data within a table |
| Delete | Deletes specified / all records from a table |
SQL Insert Command
MariaDB [example]> insert into employees (emp_id,first_name,last_name,salary,phone_number)
-> values (2,’rocky’,’deniol’,7000,5698632579);
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec)
MariaDB [example]> insert into employees (emp_id,first_name,last_name,salary,phone_number)
-> values (3,’tom’,’rogi’,4000,6987432579);
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec)
MariaDB [example]> insert into employees(emp_id,first_name,last_name,salary,contact) values (3,’Rocky’,’Joso’,10000,6985674925);

SQL Update Command
update employees set last_name=’google’ where emp_id=1;

SQL Delete Command
delete from employees where emp_id (1,3);
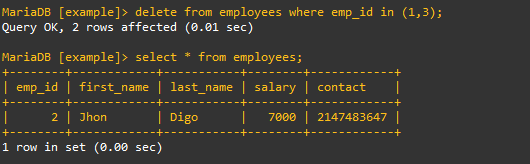
3. DCL – Data Control Language
| Command | Description |
| Grant | Gives access privileges to database |
| Revoke | Withdraws access privileges given with the grant command |
Example:
grant [privilege list] on [Database Name] to [user]
revoke [privilege list] on [database name] from [user]
Create user command
create user “demo”@”%” identified by “password”;
select user, host from mysql.user;

Give All privileges to user
MariaDB [(none)]> grant all privileges on example.* to “demo”@”%”;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)
4. TCL – Transaction Control
| Command | Description |
| Commit | Saves the work done |
| Rollback | restores database to origin state since the last commit |
| Savepoint | identify a point in a transaction to which you can roll back later |
SQL Exporting
mysqldump -u username -p database_name > output_file_path

SQL Importing
mysql -u username -p database_name < Input_file_path

How to Convert SQL Server.
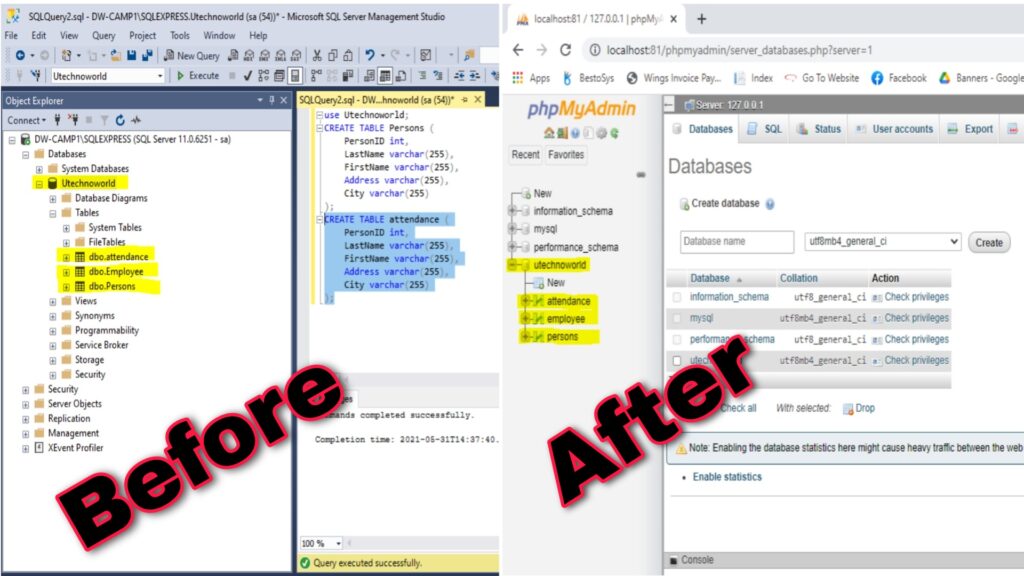
You can easily convert your SQL Database to the different platforms just flow a few steps.
Before convert SQL server we will require 3 software in your systems:
1. MSSQL Server Or Microsoft SQL Management Studio
2. XAMPP Server
3. Data Loader
4. Click here…
