What is Virtualization example ?
A Virtualization system is call as a VM “virtual machine”. a tightly isolated Application & software container with an operating system. every self-contained VM is completely independent. Putting multiple VMs on a single computer enables several operating systems and applications to run on just one physical server, or host.
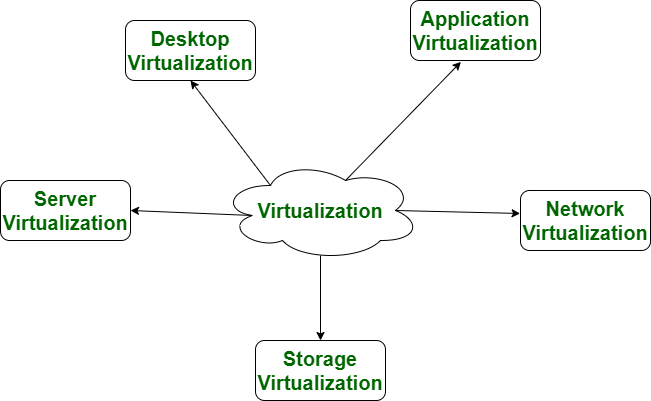
We have several type of Virtualization:
- Desktop virtualization
- Servers for virtualization
- Machine virtualization
- Network virtualization
- Storage virtualization
- Application virtualization
What is the purpose of virtualization?
It seems like everyone wants to get into the VM game And they should Enterprises had once dedicated different physical systems for every service . Actually , to ensure reliability . they may have dedicated two or more systems for each of those services .
Sure , it’s possible to configure multiple services on a single system . In fact , you might do so on the Red Hat exams . But in enterprises that are concerned about security , systems are frequently dedicated to individual services , to reduce the risk if one system or service is compromised.
Inside the Exam RHCSA (Red hat) Objectives suggest that you need to know how to
- Manage Virtual Machines
- Access a virtual Machine’s console
- Start and stop virtual machines
- configure systems to launch virtual machines at boot
- Install Red Hat enterprise Linux systems as virtual guests
What are the types of virtualization?
Desktop virtualization
Desktop virtualization is a very popular service and software technology that provides a separate desktop environment and associated application and operating systems and many other services from use of the physical systems resources. that Client used to access it.
Servers for virtualization
Server virtualization is a futuristic services because we can’t create multiple server for small business and services then it’s difficult to manage. here, require Server virtualization that dividing a physical server into multiple unique and isolated virtual servers . Each virtual server can run its own operating systems and application software independently.
Machine virtualization
Machine virtualization is quite similar to desktop and server virtualization. it also provides that kind of service but advanced. which you can create a Virtual Server and access or manage through the console. like most popular services Amazon AWS, and Microsoft Azure.
Network virtualization
Network virtualization is a method of combining the available resources in a network to consolidate multiple physical networks, divide a network into segments or create software networks between VMs.
The Network Configuration section enables you to set up IP addresses on the network cards on a target computer or virtual system. You can customize static IP addressing for a specific system or configure the use of a DHCP server.
What is the difference between a container and a virtual machine?
You may have heard of Linux container which are conceptually similar to virtual machines, but function has differently. While both containers and virtual machines allow for running applications in an isolated environment, allowing you to stack many onto the same machine as if they are separate computers, containers are not full, independent machines.
A container is actually just an isolated process that shared the same Linux kernel as the host operating system, as well as the libraries and other files needed for the execution of the program running inside of the container, often with a network interface such that the container can be exposed to the world in the same way as a virtual machine. Typically, containers are designed to run a single program, as opposed to emulating a full multi-purpose server.
Advantages of virtualization
The best thing about virtualization there has lots of Advantages.
- Lower Costs
- Easier disaster recovery
- Easier testing
- Quicker Backups
- Improved productivity
What are the types of security protocols || What is a secure network

- Point-to-point Tunneling protocol
- Secure Sockets Layer (SSL)
- Password Authentication Protocol
- Challenge Handshake Authentication protocol (CHAP)
- MS-CHAP
- MS-CHAPV2
- Extensible authentication protocol
- Kerberos

You have brought up a very wonderful details, thankyou for the post.