Expiation:
- What is artificial intelligence ?
- What is deep learning ?
- what is machine learning ?
- what is artificial neural networks ?
- What is the difference and relationship deep learning vs machine learning ?
- Types of machine learning
- Machine learning vs artificial intelligence ?
What is artificial intelligence ?
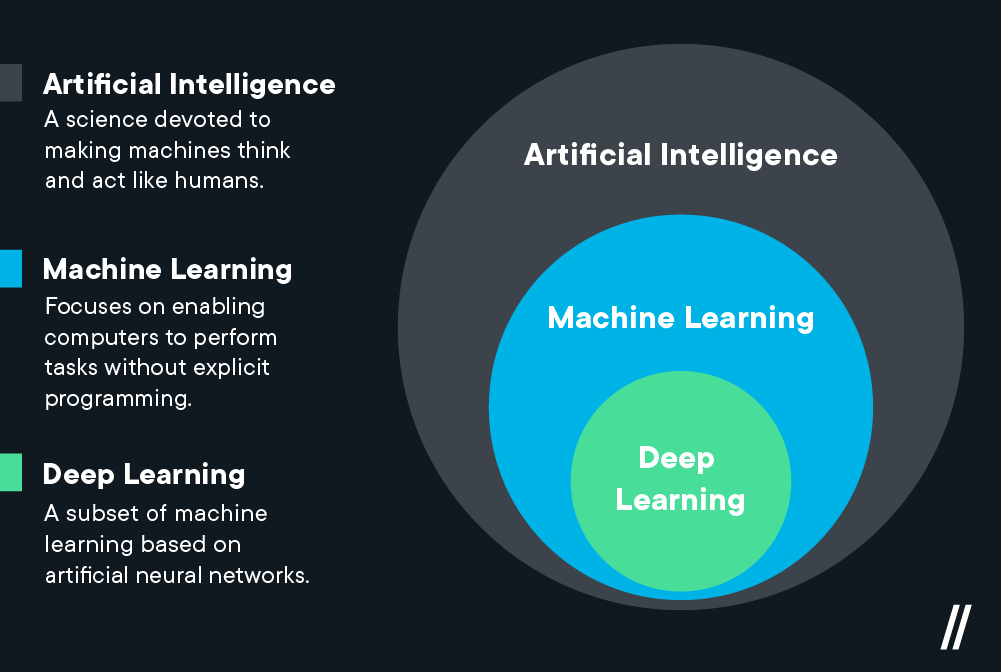
Artificial intelligence (AI) refers to the development of computer systems that can perform tasks that typically require human intelligence, such as visual perception, speech recognition, decision-making, and language translation. AI involves the use of algorithms and statistical models to analyze and learn from large datasets, enabling computers to make predictions, classify data, and automate complex processes. In short, AI aims to create machines that can mimic human cognition and behavior, and ultimately make our lives easier and more efficient.
What is deep learning ?
Deep learning is a subset of artificial intelligence that involves the use of neural networks, which are algorithms inspired by the structure and function of the human brain, to analyze and learn from complex data. Deep learning models are capable of processing large amounts of data and identifying patterns and relationships that may be difficult or impossible for humans to detect. This technology has been successfully applied to a wide range of fields, including computer vision, speech recognition, natural language processing, and autonomous vehicles, among others. In short, deep learning is a powerful approach to artificial intelligence that allows computers to learn and improve from experience, leading to more accurate and sophisticated results over time.
What is machine learning ?
Machine learning is a type of artificial intelligence that involves the use of algorithms and statistical models to enable computers to learn from data and make predictions or decisions based on that learning. In machine learning, the computer is given a set of training data and tasked with finding patterns or relationships in that data that can be used to make predictions or classify new data. This technology is used in a wide range of applications, including image recognition, natural language processing, recommendation systems, and fraud detection, among others. In short, machine learning enables computers to learn from data and make decisions or predictions, leading to more accurate and efficient processes.
What is artificial neural networks ?
Artificial neural networks (ANNs) are a type of machine learning algorithm that are modeled after the structure and function of biological neural networks, such as those found in the human brain. ANNs consist of interconnected nodes, or “neurons,” that work together to process and analyze data. These neurons are organized into layers, with each layer performing a specific function, such as input processing, feature extraction, or output prediction. During training, the network adjusts the strengths of the connections between neurons to learn how to make predictions or decisions based on input data. ANNs have been successfully applied to a wide range of tasks, including image and speech recognition, natural language processing, and predictive analytics, among others. In short, artificial neural networks are a powerful type of machine learning algorithm that mimic the structure and function of the human brain to analyze and process complex data.
What is the difference and relationship deep learning vs machine learning ?
Deep learning and machine learning are two popular terms that are often used interchangeably, but they are not the same thing.
Machine learning is a subset of artificial intelligence that involves training algorithms to learn patterns and relationships in data. The goal of machine learning is to enable algorithms to make accurate predictions or decisions on new data based on the patterns and relationships that it has learned from the training data. Machine learning can be further divided into supervised and unsupervised learning.
Supervised learning involves training a model on labeled data, meaning that each data point is assigned a label or category. The model then learns to predict the label of new, unseen data based on the patterns it has learned from the labeled data. In contrast, unsupervised learning involves training a model on unlabeled data, meaning that there are no predefined labels or categories. The model then learns to find patterns and relationships in the data without any human intervention.
Deep learning, on the other hand, is a subset of machine learning that uses artificial neural networks to learn from data. These networks are modeled after the structure and function of the human brain, consisting of layers of interconnected nodes or neurons. Each neuron processes input data and sends output to other neurons in the network.
Deep learning is particularly suited to working with unstructured data, such as images, video, and natural language, where the data is complex and difficult to work with using traditional machine learning techniques. In deep learning, the model learns to identify important features in the data by adjusting the strength of the connections between neurons.
Summary
Deep learning is a subset of machine learning that uses artificial neural networks to learn from data. While both deep learning and machine learning involve training algorithms to learn from data, deep learning is particularly suited to unstructured data and relies on artificial neural networks to identify patterns and relationships in the data. for more …
Conclusion
Deep learning and machine learning are related but not the same thing. Deep learning is a more advanced and specialized subset of machine learning that uses artificial neural networks to learn from unstructured data. Understanding the difference and relationship between deep learning and machine learning is important for selecting the appropriate approach for different applications and data types.
Machine learning vs artificial intelligence ?
Machine learning is a subset of artificial intelligence. Artificial intelligence encompasses all techniques and methods that enable machines to perform tasks that typically require human-like intelligence, such as understanding natural language, recognizing objects in images, and making decisions based on data. Machine learning, on the other hand, involves using algorithms to enable machines to learn from data and make predictions or decisions based on that learning. In essence, machine learning is one specific technique used within the larger field of artificial intelligence.
Types of machine learning
Machine learning is a subfield of artificial intelligence that involves training algorithms to learn from data and make predictions or decisions based on that learning. There are several types of machine learning algorithms, each of which is designed to solve different types of problems. In this blog post, we will explore the most common types of machine learning.
- Supervised : Learning Supervised learning is the most common type of machine learning, and it involves training a model on labeled data. Labeled data means that each data point has a corresponding label or category, such as a classification or regression problem. The goal of supervised learning is to enable the machine learning model to make accurate predictions on new, unseen data based on the patterns it has learned from the labeled data. Examples of supervised learning include image classification, speech recognition, and predicting housing prices.
- Unsupervised: Learning Unsupervised learning involves training a model on unlabeled data, meaning that there are no predefined labels or categories. The goal of unsupervised learning is to enable the machine learning model to find patterns and relationships in the data without any human intervention. Examples of unsupervised learning include clustering similar items, anomaly detection, and dimensionality reduction.
- Semi-Supervised: Learning Semi-supervised learning is a combination of supervised and unsupervised learning. In this type of learning, the model is trained on a mix of labeled and unlabeled data. The goal of semi-supervised learning is to leverage the power of both supervised and unsupervised learning to improve the accuracy of the model’s predictions. Semi-supervised learning is commonly used in natural language processing, where labeled data is often scarce.
- Reinforcement Learning: Reinforcement learning involves training a model to make decisions based on feedback from its environment. The goal of reinforcement learning is to enable the machine learning model to learn from its experiences and make better decisions over time. Examples of reinforcement learning include game playing, robotics, and autonomous driving.
In summary, machine learning includes several types of algorithms, including supervised, unsupervised, semi-supervised, reinforcement, and deep learning. Understanding the different types of machine learning algorithms is important for selecting the appropriate approach for different applications and data types.
